AQUIFER PUMP TESTING:
ESTIMATION OF HYDROLOGIC PARAMETERS WITH COMPUTER MODELING
[ ISBN 0-97411009-4 ]
$24.95 (US)
(240 Pages; Text + Illustrations)
Pursuant to Section 2725(a) of the California Code of
Regulations, a Soil and Water Investigation Phase of an environmental
cleanup (former gasoline service station site) includes the collection and
analysis of data necessary to assess the nature and vertical and lateral
extent of an unauthorized release, and the determination of a cost effective
method of cleanup. Using the information obtained during the investigation,
the responsible party must propose a Corrective Action Plan to assess
environmental impacts including but not limited to the hydrogeologic
characteristics of the site and surrounding areas where the unauthorized
release has migrated or may migrate [Cal. Code Reg. Section 2725(e)(2)].
The responsible party must conduct a feasibility study to evaluate
alternatives for remedying or mitigating the actual or potential adverse
effects of the unauthorized release [Cal. Code Reg. Section 2725(f)]. Once
the Corrective Action Plan is submitted and approved by the regulatory
agency it must be implemented by carrying out the cost effective alternative
selected during the Soil and Groundwater Investigation Phase for remediation
or mitigation of the actual or potential adverse effects of the unauthorized
release [Cal. Code Reg. Section 2726(a)].
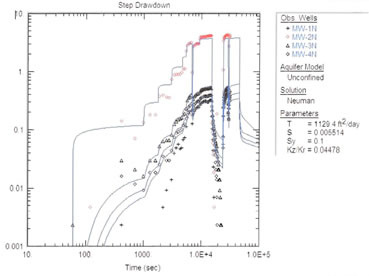
This is a report of a feasibility study to assess
groundwater velocity and pumping and treatment of groundwater to remove
dissolved contaminants. This study involves the use of a state of the art
computer program for analysis of step drawdown and constant rate aquifer
pump testing data. Nonlinear least squares parameter estimation using a
Gauss-Newton Linearization Method is utilized in obtaining the final refined
set of parameter estimates which provide a best fit of the conceptual model
to the data. The estimated parameters include Transmissivity ('T'),
Hydraulic Conductivity ('K'), Storativity ('S'), Specific Yield ('Sy') and
Hydraulic Conductivity Anisotropy Ratio ('Kz/Kr').
The estimation of the above listed hydrologic parameters
enables the caluculation of approximate groundwater velocity in the
immediate area. The rate of migration of a groundwater contaminant plume
which is primarily comprised of soluble chemicals such as Methyl Tert Butyl
Ether can be approximated according to the groundwater velocity in the
immediate area. The rate of contaminant plume migration is an important
parameter in the evaluation of impacts of an unauthorized release on nearby
public waters and waterways.
CONTENTS
Summary
I. Aquifer Pump Testing Protocol
A. Introduction
1. Objectives
B. Aquifer Pump Testing Equipment
1. Manual Measurement of Depth to
Well Water
2. Automated Measurement of Water
Column Depth
3. Pump and Effluent Discharge System
C. Step Drawdown and Constant Rate
Extraction Test
1. Step Drawdown Test
2. Constant Rate Extraction Test
D. Computer Modeling of Aquifer Pump Test Data
1. Supporting Materials
2. Software
II. Analytical Results
A. Hydrology
B. Conceptual Model
C. Visual Curve Matching (Manual Calibration)
1. Step Drawdown
2. Constant Rate
D. Automatic Curve Matching
1. Automatic Calibration; Partially
Penetrating Well
2. Automatic Calibration; Fully
Penetrating
III. Discussion
$24.95 (US)
|
| |
|